|
|
 Reference mark Reference mark
|
|
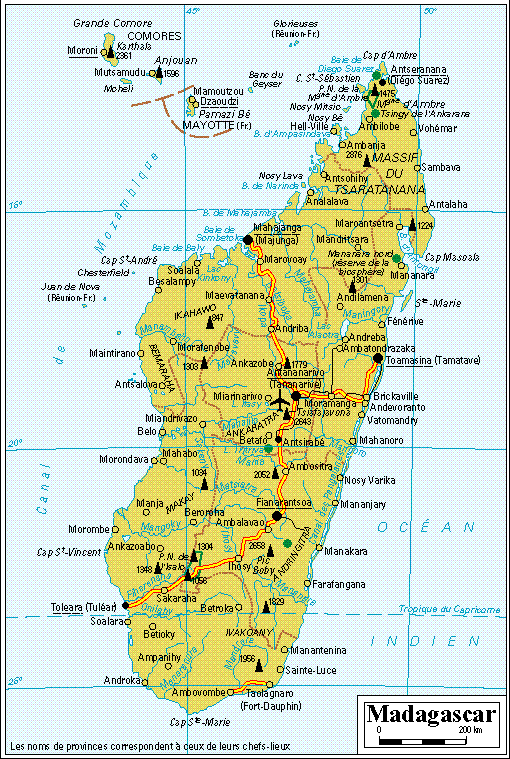
In the south-east of Africa, the largest island of the Indian Ocean. 587 040 km2 for 14 100 000 hab. Capital: Antananarivo + 2 hours in winter and + 1 summer-time compared to France (GMT + 3). 220 Volt. Drive on the right.
|
|
 Presentation
Presentation
|
1 500 km length on 600 maximum broad, the island is located in the tropical zone at 400 km of the African coasts of which it is separated by the Channel of Mozambique. It is a platform made up of hills and high plateaus (in the center) from where emergent of imposing volcanic reliefs (Tsaratana Mount: 2 876 m) primarily along the East coast. Always in the east one finds cliffs and zones of tropical forests; savannas and mangroves in the west and desert in the south. Also, several rivers running to the west to which two sedimentary basins are added, that of Majunga in the North-West and that of Morondava in the ouest/sud-west. A majority of the population, made up of 18 different ethnos groups and with 3/4 rural, is animist and practical of the ancestors; also 40 % of catholic or Protestant Christians and a small Moslem minority (5 %). It is the center and the East coast which are populated; the remainder of the country being almost deserted. The sugar, vanilla, rice, the breeding and some products mining are the main ressouces of this country which remains one of poorest in the world.
|
|
 Aperçu historique
Aperçu historique
|
- . XIIe century: installation of the Arabs on the Western coast. Previously the island was populated by populations from Indonesia then of Africa.
- 1500: arrival of the first European, the Portuguese navigator Diego Diaz.
- 1643-1674: French "Fort Dauphin" in the south of the island. At the end of the XVIIe century the island is used as reference mark to the pirates.
- XVIIIe century: the island, divided into various tribaux kingdoms, sees the domination of Mérina starting from the end of the century.
- beginning XIXe century: strong presence of English missionnaires who begins to change the country.
- 1817: Radama Ier obtains from English the title of King de Madagascar.
- 1828-1861: fold of the island on itself and political "anti-foreigners" of the queen Ranavalona I.
- 1861-1895: rebirth of the island.
- 1883-1885: the island passes under French protectorate in spite of the opposition of the queen Ranavalona III.
- 1895-1896: French forwarding, forfeiture of the Queen and annexation of the island by France.
- 1896-1905: conquest of the island by Gallieni. This one supports the rise of a kind of nationalism.
- 1946: Madagascar becomes a Territory of Overseas.
- 1947-1948: Malagasy rebellion and very severe French repression making of tens of thousands of died among the population.
- 1956: autonomy of the island.
- 1958: proclamation of the republic inside the French community.
- 1960: independence.
- 1973: exit of Madagascar of the free zone and departure of the last French troops stationed in the island.
- 1972-1993: "coup d'etat" of the army in 1972. Three years later president Ratsiraka calls upon the soviet ones. Period of socio-economic problems until the middle of the Nineties (popular revolts in 1989 and 1991).
- 1989: after the socialist experiment selected country the liberal option (privatizations, free zones...) which does not improve more the situation of the country.
- 1993: Albert Zafy is elected president with a vast majority; beginning of IIIe Republic.
- 1996: return to the capacity of Didier Ratsiraka.
- 1998-1999: desired opening of Madagascar to tourism.
- 2002: following the presidential elections disputed by the opposition to Ratsiraka and with the disorders which result from this, the state of siege is founded in the country until the departure of the former president.
|
|
 Weather
Weather
|
- Forecast for the coming days and
monthly average.
Four great climatic zones: altitude tropical climate on the highlands, wet tropical climate in the east (it rains there all the time with risks of cyclones at the beginning of year), tropical climate dry in the west and semi-arid in the south. Except to the east, the rain season goes from November to March. April-September is the best period to visit the country.
-
To envisage
Light clothing if you are on the coasts and more heats if you intend to visit the interior (high plateaus) where the nights can be very cold. Also of what to protect itself from the rain in season or on the East coast.
|
|
 Language
Language
|
- Malgache (off.), frencjh (administration language) almost into towns and touristic area.
|
|
 Currency
Currency
|
Malgache Franc and a new currency, the Ariary,
which equivalent is 5 FMG.
Exchange rate of the day.
Euros is advised (cash, travelers, card).
Travellers check and cash is exchanged without any problems. Euros are easily accepted everywhere. The credit cards are usable into specific, especially in the large hotels and the large shops, primarily with the capital. Change is only possible at bank BFV with much of waitings. Possibility also of making exchange with local people. Very easy into the airport and Tana. The changers do not hide and ask you directly. You can also change at indians or Chinese people; some accept Euros. If you leave big towns, it is advised to have local currency.
|
|










 Reference mark
Reference mark